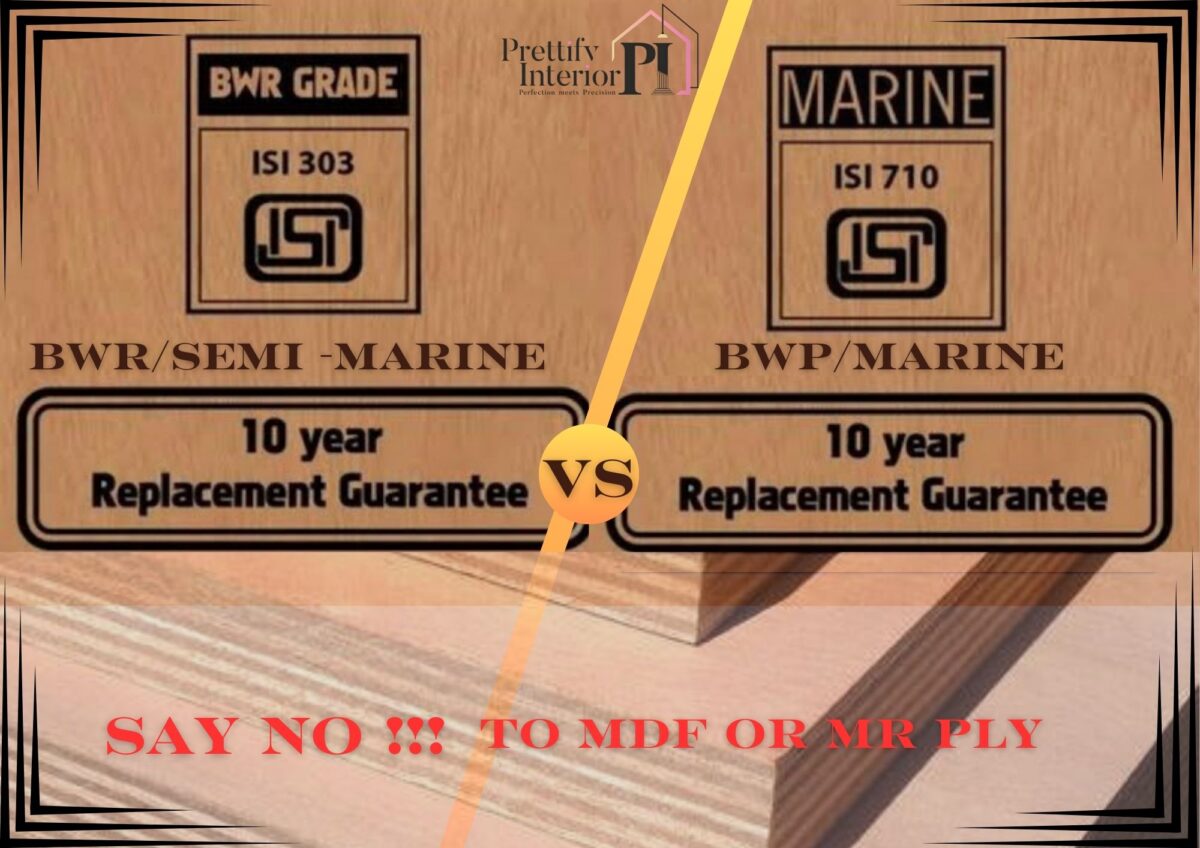
When comparing BWR (Boiling Water Resistant) Plywood and BWP (Boiling Waterproof) Plywood, it’s essential to understand their key differences in terms of composition, water resistance, durability, and application.
Technical Composition and Resin Type
- BWR (Boiling Water Resistant) Plywood is manufactured using phenol-formaldehyde resin, a synthetic polymer that imparts moderate water resistance. This resin, when cured, provides good resistance to water penetration but is not intended for prolonged submersion in water. BWR plywood typically undergoes hot-pressing with veneers glued together, where the glue line is moisture-resistant but not completely waterproof.
- BWP (Boiling Waterproof) Plywood, often termed Marine Grade Plywood, utilizes phenolic resin, which is a superior bonding adhesive. The phenolic resin is known for forming a highly cross-linked polymer matrix, making the plywood virtually immune to moisture infiltration. BWP plywood is bonded under high pressure, ensuring that the layers do not delaminate even when exposed to water for extended periods.
Water Resistance and Performance Parameters
- BWR Plywood is water-resistant to a certain threshold and performs well under IS: 303 standards. This implies that it can resist water for up to 8-12 hours without significant warping or delamination, making it suitable for areas where it may come in contact with water or humidity intermittently.
- BWP Plywood complies with IS: 710 standards, which necessitates complete waterproofing. BWP plywood can withstand boiling water for over 72 hours without structural compromise, making it the ideal choice for heavy-duty moisture-laden environments or continuous exposure to water. Its dimensional stability and durability are significantly higher than BWR, ensuring no swelling, warping, or decay.
Application in Construction and Interior Design
- BWR Plywood is ideal for interior uses in locations like kitchen cabinetry, bathroom vanities, and furniture exposed to occasional water spills or high humidity. It is suitable for interior partitions, cupboards, and modular furniture where moderate water resistance is required but full waterproofing is not essential.
- BWP Plywood is engineered for marine and exterior applications such as boat-building, outdoor furniture, garden structures, and wall cladding in buildings where full waterproofing is critical. It is also employed in sub-flooring, exterior sheathing, and locations with consistent moisture exposure, ensuring no deterioration over time due to fungi, termites, or delamination.
Manufacturing and Durability Considerations
- BWR Plywood: The core veneer and face veneer used in BWR plywood are often hardwood species, which are dimensionally stable but can experience minor expansion and contraction in humid conditions. Its resistance to decay and warping depends on the quality of the core and the glue line, which makes it a viable option for general indoor uses.
- BWP Plywood is manufactured from the highest quality hardwood veneers with uniform core bonding. The multiple cross-laminated layers in BWP plywood ensure superior strength, and its core is treated with waterproofing agents and preservatives to resist not only water but also pests like termites and borers. This makes it an excellent choice for structural durability in environments subjected to water and weather.
Cost and Long-Term Value
- BWR Plywood is relatively more affordable than BWP due to its moderate performance characteristics. While it provides adequate water resistance for interiors, it requires proper maintenance in semi-wet areas, as prolonged exposure can lead to degradation.
- BWP Plywood, being a higher grade of plywood, is priced at a premium due to its enhanced properties and manufacturing process. Its ability to resist water, rot, and environmental stresses provides better long-term value for external applications, reducing maintenance costs over time.
Standards and Certifications
- BWR Plywood conforms to IS: 303 standards, which regulate plywood intended for interior applications with moderate water exposure. The tests for BWR plywood assess its boiling water resistance for short durations, and it is certified for use in non-structural applications.
- BWP Plywood adheres to IS: 710 standards, the highest grading for waterproof plywood. This certification involves rigorous testing, including submersion in boiling water, to ensure complete waterproofing and durability in marine-grade and structural applications.
Thermal and Structural Properties
- BWR Plywood exhibits decent thermal resistance but is not suitable for extreme outdoor conditions or direct sunlight for prolonged periods. Over time, continuous exposure to harsh environmental conditions may weaken its structural integrity.
- BWP Plywood has high thermal resistance and can withstand exposure to heat and ultraviolet light, making it a superior choice for outdoor construction. Its cross-laminated structure provides added stability, reducing the risk of cracks, splitting, or warping even under extreme thermal conditions.
Conclusion:
In summary, BWR Plywood is an excellent choice for interior and semi-wet applications, where moderate water resistance is sufficient. On the other hand, BWP Plywood offers superior water resistance, making it indispensable for high-moisture environments, exterior projects, and marine uses. The decision between the two should be based on the level of water exposure, application environment, and budget.